What is Actinic Keratosis?
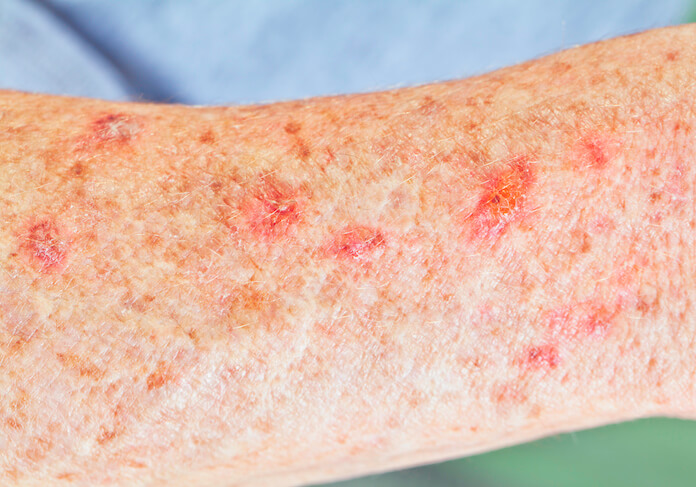
Actinic Keratosis (AK), also known as Solar Keratosis, is most commonly known as sun damage. AK’s form when the skin is badly damaged from ultraviolet rays or UV rays from sun exposure, or indoor tanning. Over time, UV rays can damage our skin and in some cases, when the damage accumulates in the skin cells, our bodies are less able to repair itself. Actinic Keratosis is often dry and scaly, pink, red or sometimes a white or brown color. If left untreated, it can significantly damage healthy skin. Untreated AKs occur mainly on the back of your hands, scalp, and face. AK’s can also be painful once the area is irritated or rubbed.
Actinic Keratosis most commonly occurs in people with fair skin, ages 40+. Those who live in places with strong sunlight, particularly places close to the equator, or people who have consistently used sun tanning beds, can see AK’s appear earlier than 40 years of age. People with weakened immune systems due to a medical condition or medications also have a higher risk of contracting this skin condition. More than 58 million Americans have one or more cases of Actinic Keratosis. One effective way to prevent this condition is to apply sunscreen on exposed areas of the skin when in the sun. When such a skin condition already exists, experts in AK dermatology recommend topical treatment solutions.



 Based on reviews
Based on reviews