What is Hyperpigmentation Skin Hyperpigmentation is the name of the patches of skin on your body that are darker than…

 Holistic
Holistic
Eczema vs Dry Skin: How To Tell The Difference
What is Eczema?
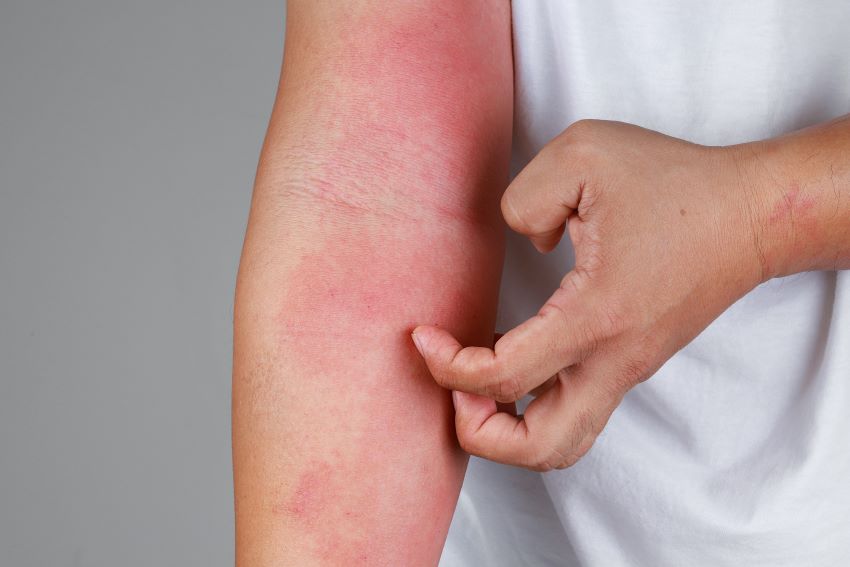
Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that results in red, dry itchy skin. Also called dermatitis, eczema can result in skin bleeding and crusting over in the folds of the arms, back of the knees, wrists, and hands. So, how do you know if you have eczema? We cover everything you need to know in this article, including eczema vs. dry skin.
What are the Types and What are the Symptoms of Eczema?
The National Eczema Association has identified seven main types of eczema. If you’ve ever wondered, “What are the symptoms of eczema?” we’re here to help you understand the symptoms associated with different types of eczema.
-
1. Atopic dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the most common form of eczema. AD is chronic that can last throughout an entire person’s life. AD is caused by the mutation of the gene that creates filaggrin. Filaggrin is a protein found in the body that creates a protective barrier on the top layer of skin. Without filaggrin, AD is more likely to develop as moisture more easily leaves the skin without its protective barrier. There are many root causes of any skin condition, however, it’s good to be aware that stress is a common trigger resulting in stress-related eczema.
- How to know if you have atopic eczema:
- Rash forms in elbow and knee creases
- Skin where the rash is may be discolored, red, or thick
- Small bumps can appear and leak fluid
-
2. Contact Dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen or foreign substance that triggers a reaction in the skin. There are two types of contact dermatitis: irritant dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant dermatitis is a type of dermatitis that occurs when the skin is injured by one of the following: chemicals (acids, alkalis, detergents, and solvents), cold/dry environments, friction (handwashing), or over-exposure to water. Allergic dermatitis is an allergic reaction that is delayed and develops one to two days after skin has been in contact with the allergen. Rashes and swelling occurs when skin comes into contact with an allergen (typically makeup, hair dye, and poison ivy)
- Symptoms of irritant dermatitis include:
- Rash and bumpy skin in the exposed area
- Burning, stinging, or itching in the affected area
- Dry patches, resembling a burn
- Symptoms of allergic dermatitis include:
- Flaky, scaly, red skin
- Hives
- Oozing blisters
- Burning or itching
- Sun sensitivity
-
3. Neurodermatitis
- Neurodermatitis occurs on one to two patches of skin. It is not widespread and results in frequent scratching of a certain area. The patches of skin itch so intensely that patients are unable to stop themselves. The scratching can irritate nerve endings which worsens the condition. If the patches do not go away, the skin protects itself by becoming thick and leathery known as lichen simplex chronicus.
- Symptoms of neurodermatitis are:
- Thick, scaly skin patches
- Patches are extremely itchy, especially when you are relaxed or asleep
- Patches bleed and get infected when scratched
-
4. Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Dyshidrotic eczema causes itchy blisters on the hands and feet. It is more common in women than men and is thought to have a genetic component.
- Symptoms are:
- Blisters on fingers, toes, palms, and soles of the feet that are filled with fluid
- Blisters are painful and itchy
-
5. Nummular eczema
- Nummular dermatitis is a different form of eczema with the main symptoms being circular, oozy, itchy patches of skin that can resemble the shape of a coin. It occurs typically when the skin experiences trauma including burns or insect bites.
- Nummular eczema symptoms appear as coin-shaped patches of skin that are discolored, itchy, and leak fluids.
-
6. Seborrheic dermatitis
- Seborrheic dermatitis appears on the body as dandruff on the scalp or yellow scaly skin on the ears and face. Seborrheic dermatitis occurs when there is excess growth of Malassezia yeast in the skin. The excess growth leads to inflammation, dryness, and itchy skin patches.
- Symptoms are:
- Skin flakes on scalp, hair, eyebrows, or beard
- Greasy skin patches covered with scales that crust on the scalp, face, ears, chest, groin, and armpits
- Red and itchy skin
-
7. Stasis dermatitis
- Stasis dermatitis, also known as gravitation dermatitis, occurs when a person has weak circulation in their lower legs. When the veins in the leg are too weak to push blood back to the heart, the veins leak fluid. This results in swelling, redness, and itchiness in the area where fluid is leaking.
- Stasis dermatitis can be easily diagnosed if symptoms are as follows:
- Swelling in the lower part of the legs
- Varicose veins in the legs that are thick and damaged
- Skin over those veins is dry and itchy
- Open sores can develop on lower legs and tops of the feet
Eczema vs. Dry Skin
While you might mistake dry skin for eczema there are some key differences to recognize before reaching out to a doctor. If you experience dry skin and some itchiness after common triggers you are most likely just suffering from dry skin. Some common things that can result in dry skin are skin having direct contact with cold windy weather, dehydration, or little to no use of moisturizer will leave your skin very dry. However, if you find your skin being dry for uncommon or unknown reasons with an extreme amount of itchiness, this is likely some form of eczema.
When to See a Doctor About Eczema
When your symptoms become too uncomfortable and you find that home remedies are not doing the trick to ease your symptoms, you should contact your dermatologist or go to your nearest eczema pharmacy. Once they view the symptoms, your doctor will develop a treatment plan to get rid of the eczema symptoms. If your child is suffering from eczema, we discuss eczema treatment for kids in our helpful guide for parents.
Treatment for Eczema
The most common and most effective treatments include:
-
OTC Products
- Topical over-the-counter products to treat eczema are typically moisturizing, anti-rash, anti-itch, and gentle skin cleansing products to prevent infection.
-
Bathing
- Treating dry skin and eczema patches in the simplest form is to bathe and soak the skin in a warm bath and moisturize the skin immediately afterward. Additionally, adding specific ingredients like vinegar, oatmeal, and baking soda to the bath can help to calm the skin.
-
Prescription Products
- For more severe eczema flare-ups, your dermatologist may prescribe dermatology medications like topical corticosteroids, PDE4 inhibits, skin barrier creams, or topical calcineurin inhibitors. Another common treatment is the use of hydrocortisone for eczema. All these products should be applied topically to relieve the redness, dryness, and itchiness in the skin.
-
Light Therapy
- Light therapy involves a machine that emits controlled levels of ultraviolet B light on the skin to reduce inflammation and itching caused by eczema.
-
Systemics
- Severe eczema can be treated by immunosuppressant medications. These help to suppress the immune system to slow down intense eczema flare-ups.
-
Biologics
- Biologics are drugs that target a part of the immune system that contributes to eczema symptoms. The drugs are administered intravenously to immediately target that part of the immune system that is triggering eczema.
Sources
This blog is based on research and/or other scientific articles and is written by our experienced Chief Strategy Officer and Pharmacist, Ronak Desai. This blog is fact checked by our educated Pharmacist in Charge, Darshan Patel, who additionally runs our Apotheco Manhattan location.
Here at Apotheco Pharmacy Group, our goal is to provide the most up to date and accurate information on health and dermatology related topics. We do this to ensure our readers can make informed decisions based on factual content. All blogs undergo an extensive review process before posted.
This blog contains trusted sources. All sources are listed at the bottom of this article with hyperlinks that take you directly to the source.